The truth and lies about the lie detector.
Can this employee be trusted, does it make sense to promote him up the career ladder?
How will a person behave in a critical situation, what is the motivation of a job candidate, who is involved in an illegal act?
All these issues play a critical role in ensuring business security, from the point of view of the «human factor».
Currently, when ensuring security, the main attention is paid to technical means (security alarms, access control, total video surveillance, etc.). However, the “human factor” is no less important.
For example, a job candidate has «weaknesses» (alcohol, drugs, gambling addiction).
In another case, a working employee intends to use his official position for personal purposes and knows how to «bypass» existing security systems.
Finally, any responsible employee can become a victim of destructive psychological influence and make a mistake in making an important decision.
You can't label a person as a reliable and loyal employee once and for all and rest on that.
It is necessary to conduct an assessment of the reliability of employees upon hiring, and also to systematically monitor it.
This requires a set of measures that would successfully solve the above-mentioned problems quickly, efficiently, reliably and throughout all or part of the employee's term of employment.
It should be noted that the issue of reliability and predictability of people working in an organization, despite its relevance, is sometimes ignored by specialists ensuring security, due to the uncertainty of the means and methods for solving it.
Today, the first thing that comes to mind when problems with the «human factor» arise is the polygraph (lie detector). Thanks to the media and cinema, it has gained notoriety. There is a widespread image that a lie detector is a device that can sign a verdict with a high degree of certainty based on physiological reactions: whether a person is guilty or not. Polygraph examiners themselves support the spread of this myth, demonstrating «convincing» tricks with guessing the intended numbers or cards and talk about the reliability from 80 to 95%.
As part of such a trick, you will be asked to think of one number or card out of, say, five, and during the polygraph test to the question — «did you think of a number (card) …?» always answer «no», respectively, you will lie once, which the polygraph examiner should detect. If you want to stump the polygraph examiner, ask him to change the experiment a little, for example, always answer «yes», respectively, you will lie 4 times and tell the truth once, let him now try to figure out — where is the truth and where is the lie. You can complicate the experiment, think of 20 numbers out of a hundred, here the polygraph examiner will categorically refuse to demonstrate sleight of hand.
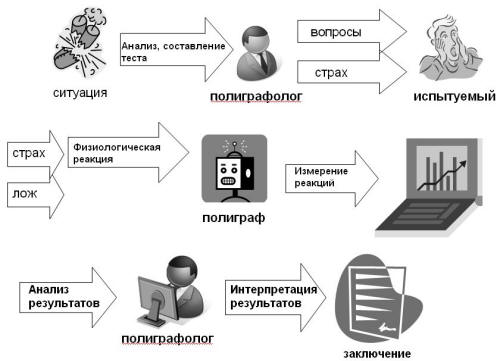
Let's figure out how the polygraph works, or rather the polygraph examiner. Let's pay attention to Figure 1.
Let's say there was some explosive situation that caused damage to the organization. The polygraph examiner analyzes the specifics of this situation, identifying nuances that only the person who committed the act can know and composes a questionnaire taking into account the phenomenon of the so-called «criminal knowledge». Then the most interesting thing happens — before starting the survey, the polygraph examiner must initialize, i.e. instill fear in the subject of the polygraph. This is one of the main secrets of the lie detector — if a person is not afraid of the polygraph, then he will not give reactions. And instilling fear is a special kind of art and the success of the test largely depends on this.
Next, in accordance with a certain algorithm, the subject is asked questions. It would seem that everything is simple, however, only at first glance. Today, there are a certain number of methods and theoretical directions in lie detection. Both law enforcement agencies and commercial firms are engaged in the development of these methods. These methods and organizations are in fierce competition with each other, which often takes incorrect forms. Therefore, if you encounter a polygraph examiner, ask what theoretical and methodological direction he belongs to.
So, the subject answers questions and at some point tells a lie. There is a hypothesis (only a hypothesis) that when telling a lie, a person experiences certain emotions (in our case, the fear of being exposed), another hypothesis says that emotions cause a change in physiological reactions, which is what the polygraph actually measures.
Here we can be absolutely sure that the polygraph hardware will record these changes with high reliability, but only with a small «but». We cannot be sure that these changes were caused by the question asked, that is, the outburst of emotions could have been caused by other factors (let's say you remember a funny joke). Further. It is not a fact that the change in physiological reactions occurred as a result of emotional experiences, maybe you wanted to sneeze or something else, by the way, many methods of counteracting polygraph tests are based on this.
In fairness, it should be said that polygraph examiners fight the influence of random factors, ask the same question several times, as a result of which the testing lasts 2-3 hours. It is worth noting — if they are not too lazy to do this. And such cases are common, we will talk about this below.
Then the polygraph, in accordance with the measured reaction indicators, plots curves of their changes. In essence, a modern polygraph is fundamentally no different from the one created in 1914, when the curves were drawn by a recorder on paper; of course, today it is much more convenient to view graphs on a computer. But even here, everything is not so simple.
There are polygraph models from different manufacturers that compete fiercely on the market, and naturally, each manufacturer praises its products and belittles the others. Therefore, if you decide to purchase a polygraph, do not forget to check with the manufacturer about its functionality and design differences from models from other manufacturers.
Returning to the polygraph testing procedure, we will tell you how a polygraph examiner analyzes the results and makes his conclusion.
Naturally, the specialist analyzes the results based on his knowledge, skills, experience, subjective preferences, situational mood, physical health, interpersonal relationships with his spouse, the amount of the bribe — one can continue listing all the «human factors» to which the polygraph examiner himself may be subject. But let's move on to the conclusion.
Some customers of polygraph tests require the specialist to make an unambiguous conclusion: a thief is not a thief, a «snitch» is not a «snitch», sent or not. Many polygraph examiners follow the lead of the customer, although they know that no method can sign a sentence.
The test results are an additional reference point for further development and can give impetus to work with this person using other methods in the right direction.
There is another extreme, when the polygraph examiner in his conclusion only gives formulations of the following plan: «the reactions of subject A to question B with 89.4% reliability indicate the falsity of the answer.» This is already something from the realm of advertising claims that your hair will become 93% more attractive. That is, the figure is impressive, but there is zero useful information.
To sum it up, we can say that a polygraph is a good tool in the hands of a very good specialist. But has anyone ever tested the specialist himself?
It is worth mentioning such an exotic thing as a voice lie detector. It would seem obvious that a person's stress or anxiety is reflected in the characteristics of the voice, but the manufacturer does not disclose which parameters are identified and by what algorithms they are processed. Therefore, it is difficult to discuss something that is unknown how it works and whether it works at all.
Another technology for working with the risks of the «human factor» is the hardware and software complex of computer psychosemantic analysis MindReader. The scientific nature of the name indicates that this is the fruit of the work of scientists and specialists who worked in closed laboratories of the Soviet Union, which is currently freely distributed and is not, unlike the polygraph, special equipment. Since this technology is still widely known only in narrow circles, we will dwell on the principles of its operation.
The testing procedure on the MindReader APCS consists of the following: the subject is presented with stimuli on the monitor screen in an unconscious mode (i.e. very quickly – 14 ms): words, short phrases or images grouped by topic. As a result, the person does not have time to read the words and comprehend the images, but the psyche perceives them on a subconscious level and reacts.
The reaction time is recorded using a special sensor.
If the stimulus is significant and relevant for the subject, this leads to a deviation of the reaction time from the average. Visually, the subject is aware of and observes on the monitor screen only the change of rows of random numbers or meaningless mosaic pictures and does not guess about the purpose of testing.
Under these conditions, the subject does not even have to lie, the information is read in its pure form, this is a kind of «truth detector».
The hardware and software implementation of this method allows an HR or security service employee to independently develop tests for existing tasks and conduct surveys. The test is fully automated and does not require special knowledge from the APCS operator.
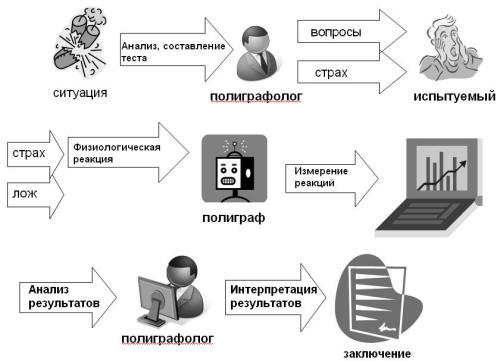
 Let's consider the algorithm of operation of this complex (Fig. 2). As in the case of a polygraph, an internal investigation is conducted in the organization based on a critical situation. The responsible security officer analyzes the situation, finds out the circumstances of the case and, based on the data obtained, compiles a set of stimuli. The set of stimuli is a description of what happened in words, short phrases or images (for example, photographs of the scene, weapons, portraits of possible accomplices, etc.). This is the only creative component in this method, which is especially easy for former operatives to handle.
Let's consider the algorithm of operation of this complex (Fig. 2). As in the case of a polygraph, an internal investigation is conducted in the organization based on a critical situation. The responsible security officer analyzes the situation, finds out the circumstances of the case and, based on the data obtained, compiles a set of stimuli. The set of stimuli is a description of what happened in words, short phrases or images (for example, photographs of the scene, weapons, portraits of possible accomplices, etc.). This is the only creative component in this method, which is especially easy for former operatives to handle.
Then the set of stimuli is entered into a computer program, and it automatically generates a test. This is where the role of the specialist in the research procedure ends.
Then the subject is asked to undergo a certain test on the computer, but its true purpose is not revealed, the whole procedure is described as a test of performance, concentration, fatigue, and, indeed, it looks like that.
When a series of meaningless numbers or mosaic pictures appear on the screen, the subject must press a special button as quickly as possible.
In reality, stimuli related to the case under investigation are briefly presented on the screen before these signals, and the subject does not suspect anything. If the presented stimuli have great emotional significance for the subject, as evidence for a criminal, then this leads to a change in the time of pressing the button.
The program automatically measures the reaction time, performs statistical processing of the results obtained and forms a protocol. It is clear that in comparison with the polygraph, the role of the specialist in this method is reduced to a minimum.
What else does scientific and technical progress in the field of lie detection have in store? We have all heard the popular expressions: «The eyes are the mirror of the soul» and «The eyes do not lie.»
Some people have the ability to determine lies by the eyes, and only now has the technical ability to automate this process appeared (Fig. 3). It is known that developments in this area are being carried out by US intelligence agencies, as well as by enthusiastic scientists in Russia. Let's figure out what the features of eye movement are.

Eye movement analysis is a popular area of research in modern science. Specialists studying vision processes unanimously agree that the eyes are the brain brought forward. That is, the eyes directly reflect the thought processes that occur in the brain. Eye movement analysis is conducted in two directions. The first is the analysis of movement depending on the proposed visual stimuli (for example, advertising posters). For example, it has been proven that eye movements differ from each other when perceiving attractive and not very attractive images.
The second direction is the analysis of movement depending on internal thought processes. It does not matter where the person is looking. Let's say a person is deep in thought, his gaze is directed «inward» and he does not see what is happening around. It has been experimentally confirmed that it is possible to measure thought processes (for example, making a difficult decision) and the psychological state (anxiety) of a person by the nature of eye movements.
Most of us believe that eye movements are smooth. However, upon closer examination, we are convinced that eye movements are a change of stops (fixations) and jumps of the eyes, i.e. the eyes make so-called saccadic movements.
Information is perceived only at the moment of fixation. They account for most of the time (92–94%) during perception, the rest is taken up by jumps, i.e., moving the gaze from one section of the visual image to another. In this case, the eyes act like a movie camera. They seem to shoot still frames, and then project them onto the screen (into the brain). The impression of continuity is created by the ability of the eyes to preserve the visible image on the retina. The duration of fixation is made up of the time required to perceive a section of the image and the time required to comprehend it as part of the whole.
A person is usually not aware of eye movements. One of the reasons for this is the lack of so-called conscious, voluntarily controlled feedback, through which messages about micro eye movements would be transmitted to the brain.
A person learns about the direction of his gaze only from the position of the observed objects and under the influence of some other factors, such as turning or tilting the head. However, involuntary eye movements play a large role in visual perception.
It is no coincidence that researchers, assessing the complex of processes occurring in the human visual system, note: «We often do not know what we see until we know what we are looking at.» When looking at a certain object, the eye makes regular jumps along its contour with a frequency of 2-5 times per second.
The duration of fixations largely depends on the complexity of the activity. In this case, we mean the external plan of activity associated with information search and perception of visual information.
In addition to fixations, which imply the immobility of the gaze and, accordingly, the eyes, relative to some external object, there are slow, drifting eye movements, leading to a shift in gaze across the object.
The disclosure of more complex mental processes occurs in a case that can be described as «detachment from the situation», «mental representation», «inner gaze», «inner vision». These metaphors characterize mental activity on the internal plane. At the same time, everyone knows the phenomenon when in deep thought a person «looks, but does not see», i.e. the eye fixes some object, but the person does not notice it.
Thus, the eyes are a direct reflection of thought processes. The peculiarities of eye movement are not affected by either the emotional state of a person or his psychophysiological reactions. Eye movement analysis is a direct information channel for obtaining information about the mental operations performed by a person.
Before lying, a person must do some mental work, and in doing so, he switches from the external to the internal plane of activity, which is clearly manifested in a change in the nature of eye movements.
The use of modern hardware and software systems makes it possible to directly receive information about the sincerity of the interlocutor during a specific situation (an interview with a job candidate, business negotiations), and it is also possible to analyze previously made video recordings.
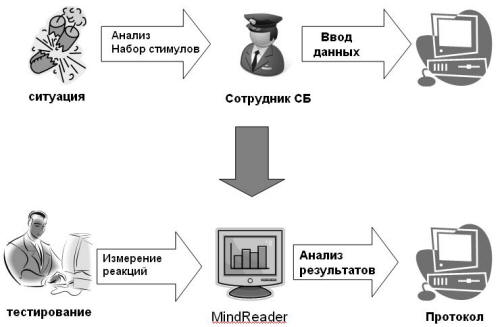
 Let's consider the scheme of operation of such a complex using the example of business negotiations (Fig. 4). A hidden high-speed megapixel video camera records the face of the interlocutor. The video stream is sent to the computer, then special software digitizes it and recognizes the location of the eyes and their movement, then the program determines the features of the eye movement trajectory using a special algorithm, and if it indicates a lie, the program will give a special signal.
Let's consider the scheme of operation of such a complex using the example of business negotiations (Fig. 4). A hidden high-speed megapixel video camera records the face of the interlocutor. The video stream is sent to the computer, then special software digitizes it and recognizes the location of the eyes and their movement, then the program determines the features of the eye movement trajectory using a special algorithm, and if it indicates a lie, the program will give a special signal.
It seems that this technology has certain advantages: firstly, lie detection is carried out covertly and remotely, secondly, this happens directly at the moment the situation develops and, thirdly, the role of the «human factor» of the specialist himself is reduced to zero.
Of course, each of the presented technologies has its own advantages and disadvantages and cannot be universal for solving absolutely all problems related to the «human factor» (professional selection, preventive work with personnel, official investigations, etc.). The scope of possibilities and tasks solved by these methods overlap in many ways, but at the same time, each method has special features inherent only to it.
M.A. Konobeevsky.
Truth and lies about lie detection (MiB No. 6/2008)
Trust must be earned,
the trusted can be bought.
V. Chermak-Novina