Intelligent buildings — from practice to theory.
Author: Volkov A.A. Doctor of Engineering Sciences, Professor, Dean of the Faculty of ISTAS MGSU
The article continues a series of publications presenting the foundations of the promising science of designing “intelligent” buildings, directly aimed at eliminating the existing methodological gap between practice and theory in creating building automation systems and structures of all levels (see AZ Bulletin, No. 5, 2006; No. 6, No. 7, 2007).
The original paradigm of innovative homeostatic design of buildings and structures is considered.
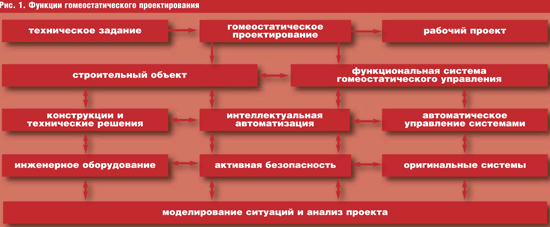
Let us consider the basics of the methodology of innovative homeostatic design of buildings and structures. In accordance with the definition given in the previous article and its interpretation in the aspect of the accepted scientific and technical hypothesis, the functions of homeostatic design can be classified as solving problems in two main areas: designing the actual construction object and designing functional systems of homeostatic control of this object (Fig. 1).
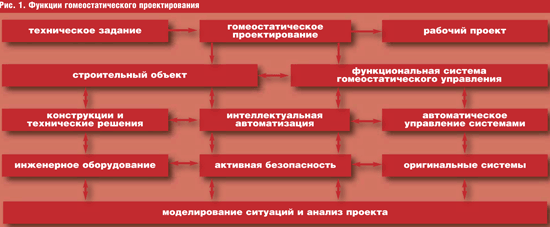
Homeostatic design of a construction project involves the design of structures, engineering equipment, technical, technological and other solutions for a building (structure) and/or its elements, aimed at supporting the functions of intelligent automation and active safety of construction projects at all levels.
Design of functional homeostatic control systems involves the development of automatic control elements for a wide range of existing systems and the creation of original systems of intelligent automation and active security of buildings and structures, as well as a comprehensive monitoring system.
Homeostatic design is the basis of the methodology for modeling situations and analyzing a project, which represents a comprehensive analytical approach to identifying project elements that can, in one form or another, initiate and/or prevent the suppression of the dynamics of an abnormal situation, and developing schemes for forming solutions to optimize such elements. Within the framework of the proposed methodology, preliminary mathematical modeling, analysis and multi-criteria assessment of possible (probable) disturbances, their dynamics and consequences are carried out on the basis of a formal information model of a construction project created at the stage of homeostatic design.
An information model of a construction project is a set of knowledge about the structures, engineering equipment, technical, technological and other solutions of a building (structure) and its elements, formalized in terms of describing the construction project as an object of target management.
Formation of decisions on project optimization according to safety criteria of operation of buildings and structures is built in the context of appropriate mathematical foundations, use of information base of analogies of project solutions and expert assessments. Such approach is intended to increase objectivity of independent assessment of the project according to the specified criteria.
The basis for information support of the processes and results of homeostatic design is a set of information support for computer-aided design systems (CAD) of buildings (structures) and their elements. Indeed, only CAD systems are a source of formalized data on design, technical, technological and other solutions used in the construction of a specific object. Original CAD-based application software, expanding the capabilities of the solutions used in terms of designing engineering equipment and other systems of a building or structure, uses and supplements CAD data. Another argument in favor of this approach is the availability of stable formats for presenting and classifying CAD data, the expanded use and conversion of which is a task successfully solved today at the level of building software systems. Thus, CAD data are the information basis for building a formal model of a construction object, as well as creating new and designing elements of automatic control of existing systems in a complex of intelligent automation and active safety tools for a construction object. It should be noted that there are obvious prospects for using existing automation systems and technologies in new project practice.
In addition, many tasks of preparing project, operational and other documentation and data, creating structures for describing subject areas, storing and using subject information have already been solved in accordance with existing standards.
The concept of functional systems of homeostatic control presupposes situational modeling of processes that determine the dynamics of disturbance. Formally, the task of controlling a hypersystem as a whole can be reduced to constructing, in a sense, expedient sequences of global disturbances and associated global controls. Obviously, not every control is applicable in an arbitrary situation: it is impossible to choose a sequence of controls that could be used independently of the sequence of disturbances. Thus, it is necessary to look for not a sequence, but a control strategy (see the formal basis above), i.e. to unambiguously determine which of the controls should be used in each of the situations whenever this situation arises. The chosen strategy presupposes the construction of a certain set of homeostatic control scenarios.
Homeostatic control scenario is a directed sequence of actions (strategy) implementing homeostatic control functions, changing the actual functional and/or technical characteristics of the control object as a response to such actions. Homeostatic control scenarios for a construction object are formed at the stage of homeostatic design.
Practical implementation of building and structure management functions in the sense described above is a task solved by means of and on the basis of functional systems of homeostatic management of a construction site, representing a complex of interconnected information, analytical, technical, technological and other solutions implementing the functions of homeostatic management of a building (structure) and its elements. Functional systems of homeostatic management of a construction site are designed on the basis of system integration of standard and original solutions. The basis of such integration are CAD environments, a complex of auxiliary application software based on CAD, electronic documentation systems, automated systems for managing construction and technological processes and other modern information and telecommunication technologies.
Obviously, the presented methodology determines the need to create unique components of functional homeostatic control systems. Unique components of such systems are blocks for modeling situations and project analysis, situational modeling, forming strategies and scenarios of homeostatic control, as well as solutions implementing the concept of homeostatic monitoring of buildings (structures) and their elements — permanent analytical control of compliance of observed functional and/or technical characteristics of the object and/or its elements with established values and processes of changing actual characteristics, carried out in real time.
Based on the proposed concept, the structure and composition of the integrated monitoring system are formed, the design of which is carried out by means and at the stage of homeostatic design of buildings and structures, which allows taking into account the features of a specific object. The main task of the integrated monitoring system of a construction site is to support the processes of information afferentation (a permanent flow of thematic information coming from the elements of the control object to the elements of the control system) and elements of systems implementing the processing of feedback, i.e. reverse information afferentation (information flows reflecting the reaction of the control object to the elements of the control system actions and the dynamics of disturbance initiated by these actions).
The concepts of “direct” and “reverse information afferentation” are defined in accordance with the concepts of “direct” and “reverse afferentation” proposed by Academician P.K. Anokhin within the framework of the theory of functional systems. He especially emphasizes that “no attempt to understand the general architecture of adaptations, and even more so to model any vital manifestations, can be considered sufficient if it does not properly take into account the principles of organizing the body's functional systems: afferent synthesis, action formation and reverse afferentation of its results” (P.K. Anokhin, “Selected Works: Cybernetics of Functional Systems”).
The methodology of homeostatic monitoring of buildings (structures) and their elements involves dynamic control of the structures and composition of information components of functional homeostatic control systems in terms of objective assessment of the main parameters of information flows.
It should be emphasized that one of the main principles of designing functional homeostatic control systems for a construction site is the system integration of standard and original (unique) components at all levels. Designing information flows based on standard solutions allows for increased efficiency in creating a complex of information and technical systems, which facilitates the practical implementation of the presented theoretical concept.

Добавить комментарий